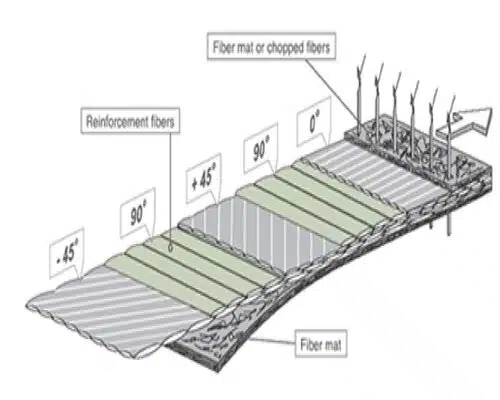
SKAPS Multiaxial fabrics are non-crimp, multi-axis, and multi-layered reinforcements. Layer count, orientation, weight, and fiber content of the layers vary and are based on the product line and application.
The layers are stitched with polyester yarn. Fabrics can be produced using multiple layers (0°,90 °,+45°,-45°), as well as combined with chopped mat and multiple layers of the veil and/or non-woven materials.
Typical applications for these Non-Crimp Fabrics are wind energy, marine/shipbuilding, sport/leisure products, automotive, aerospace & defense, FRP Poles, Water park slides, architectural designs etc.
Unidirectional Fabric:
A unidirectional (UD) fabric is one in which the majority of rovings run in one direction only. A small amount of rovings may run in other directions with the main intention being to hold the primary fibers in position, although the other fibers may also offer some structural properties. Some weavers of 0/90° fabrics term a fabric with only 75% of its weight in warp direction as a unidirectional, whilst for others, the unidirectional designation only applies to those fabrics with more than 90% of the fiber weight in the warp direction. The UD fabrics have high longitudinal strength.
Unidirectional fabric can be made as 0° orientation or 90° orientation.
Double Bias or Bi-Axial fabric :
Double Bias fabrics are continuously roving oriented in the +45° and -45° directions into a single fabric. Double Bias Fabrics offer superior structural performance in applications subject to extreme shear and torsion stress. These properties are ideal for applications such as wind blades, marine panels, and snowboards.
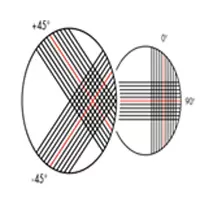
Bi-Directional Fabric :
The bidirectional fabric (0° & 90°) made by stitching two layers is different from woven fabric (0° & 90°). The stitched bi-directional fabrics are NON-CRIMP FABRICS, which means rovings won’t be interlaced as woven fabric. Woven fabric composite tends to fail in high fatigue due to the crimp. This stitched bidirectional fabric avoids the problem and provides excellent fatigue resistance. Another comparison of woven and the stitched fabric is that higher GSM woven fabric consumes more resin than stitched fabric due to crimp. This obviously increases the production cost of composite manufacturing.
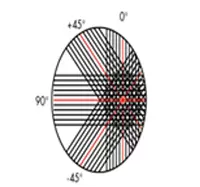
Triaxial Fabric :
Triaxial fabrics are a three-layer construction fabric, there are two styles of Triaxial- one has a fiber orientation of (+45°/90°/-45°) and the other has a fiber orientation of (0°/+45°/-45°). Triaxial fabrics are used for high-strength applications.
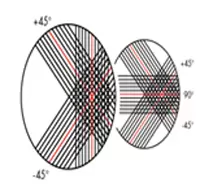
Quadraxial Fabric :
Quadraxial fabric consists of all layers (0°/+45°/90°/-45°) of roving orientation. This fabric provides strength in all directions. And this fabric can be produced with the maximum aerial density when compared to any other fabric style.
Technical Data Sheets
Applications
Resources