Impoundments, Industrial Lagoons, and Engineered Ponds are artificially created fluid and water management and storage systems, which are more and more commonly engineered and designed using geosynthetic materials versus relying on the performance of compacted native clays or the complex processes of bentonite amendment to native soils.
Ponds can be of various types depending upon applications such as:
- Decorative and Landscape Ponds
- Animal and Livestock Drinking Ponds
- Livestock Manure Management Ponds
- Fire Control Ponds
- Evaporation Ponds
- Irrigation Ponds
- Geothermal Ponds
- Leachate Ponds
- Wastewater Ponds
- Raw Water Storage Ponds
- Mining & Pregnant Solution Ponds
Why SKAPS Geomembrane for Ponds
- Superior barrier compared to naturally occurring materials or other lined solutions
- Easily weldable to existing liner for future expansions
- White surface option offers extra benefits of reduced wrinkles and lower surface temperature
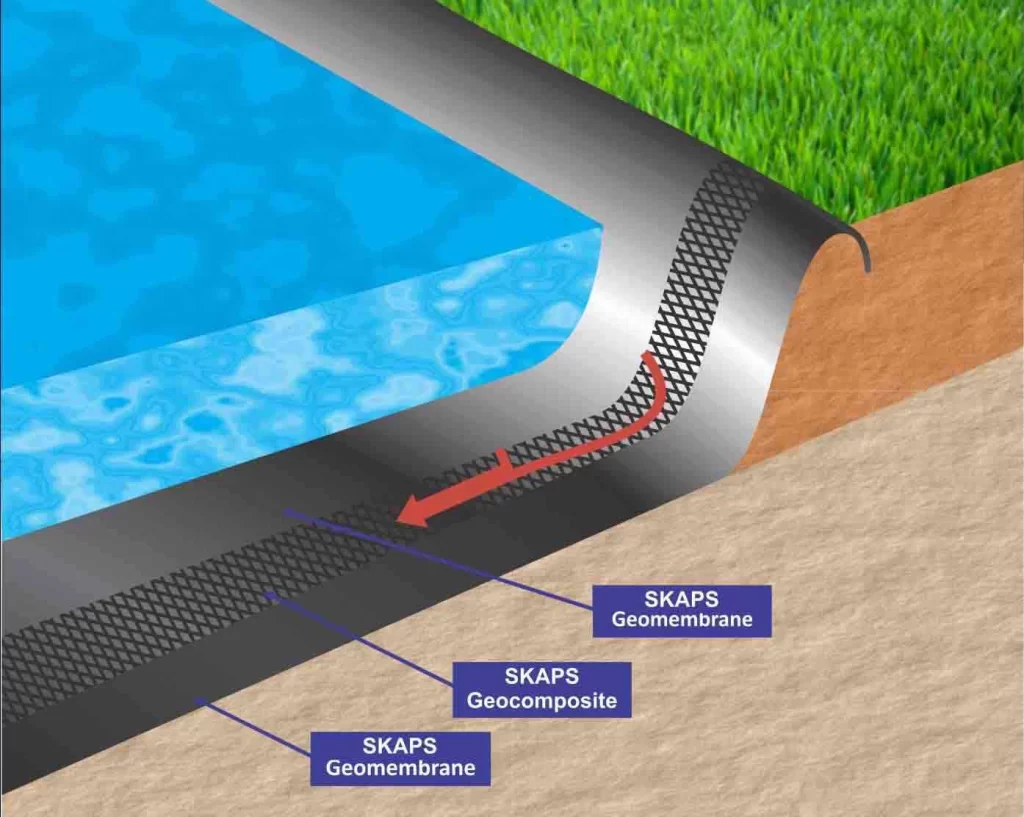
SKAPS Geomembranes used in Ponds
Why SKAPS Geonet and Geocomposite for Ponds
- SKAPS geonet and geocomposite are great drainage options for low slopes and can also withstand high loads which makes an ideal system by providing drainage to migrating gases and liquids.
- SKAPS geonet and geocomposite offer better protection to geomembrane and are the most cost-effective solution for drainage in pond applications.
Major Concerns of Pond Engineering and Construction
- Groundwater drainage During the construction of ponds, underground running water, and water tables may be intercepted, which must be drained to eliminate the hydrostatic pressure and guarantee the stability of the structure.
- Capture and mitigation of gases SKAPS geonet and geocomposite provide better gas drainage solutions beneath ponds. Often the subsoil has entrapped gases that travel upwards and accumulate beneath the impermeable barrier such as geomembrane. These gases create uplift pressure on the impermeable barrier which can ultimately affect the integrity of the impermeable barrier and destabilize the pond systems.
